I. Core Principles
Water Wedge Effect: ? When ultra-high-pressure water jets (typically above 2000 bar / 30,000 psi) impact the surface of rust or coating at extremely high speed, water molecules instantly penetrate the tiny gaps between the rust/coating and the metal substrate, or the pores within the rust layer.
Impact Separation: ? Water rapidly expands in the gaps, generating immense pressure (water hammer effect). When this pressure exceeds the adhesion between the rust/coating and the substrate, or the strength of the rust layer itself, it separates the rust or coating from the substrate.
Shear Scouring: ? The high-velocity water jet itself possesses powerful kinetic energy, directly scouring and removing separated debris and loosely attached rust from the surface.
Pure Physical Action: ? The entire process relies primarily on the physical energy of water (pressure and kinetic energy), without the use of chemical solvents or abrasives (pure water jet). Therefore, it does not produce chemical reaction residues or introduce new pollutants (such as abrasive dust).
II. Main System Components
Water Source: ? Provides clean water (tap water, industrial water, treated water). Water quality affects pump lifespan and nozzle wear.
Pre-filtration System: ? Removes solid particles from the water, protecting the high-pressure pump and nozzle.
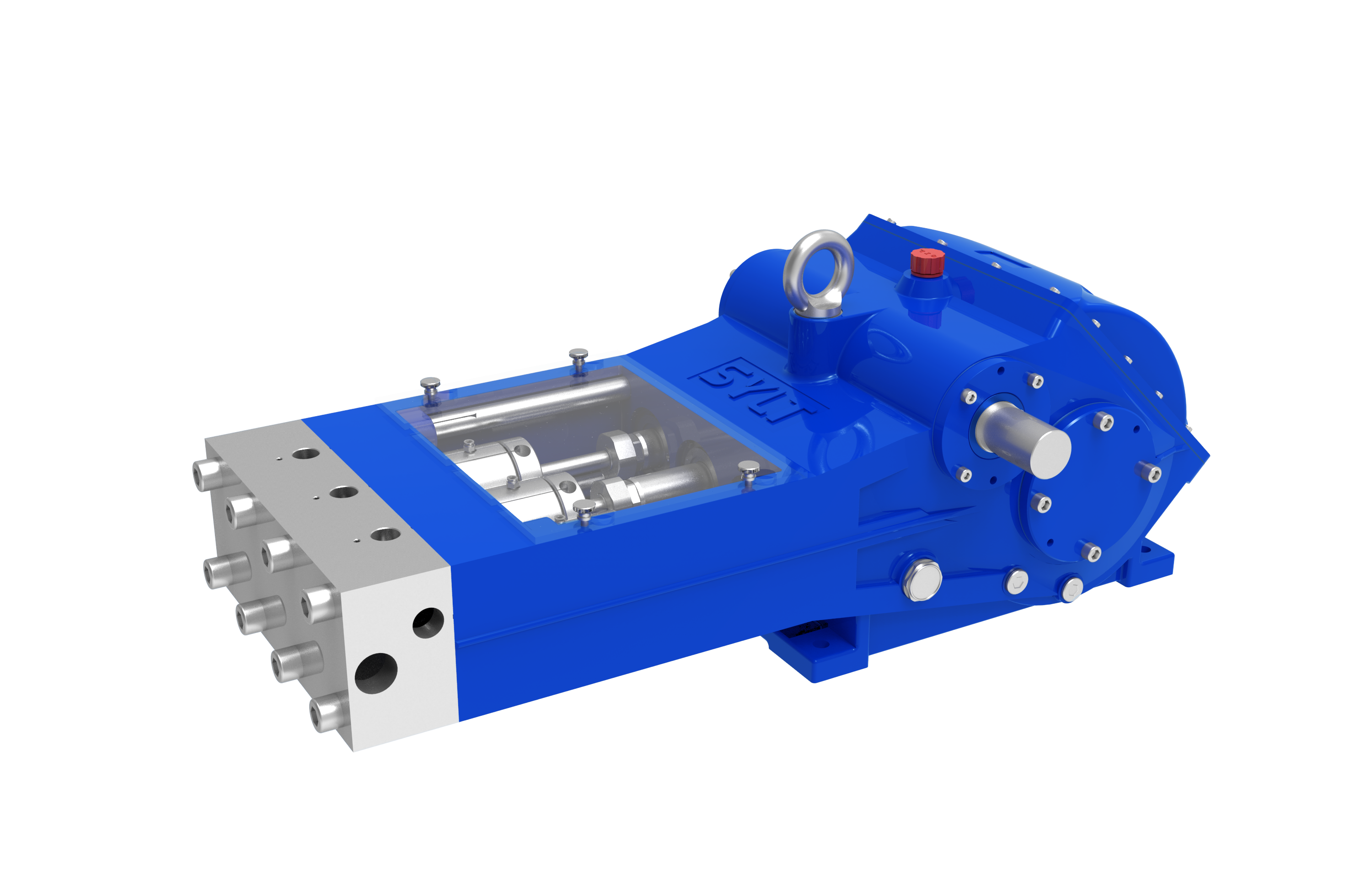
High-Pressure Pump: ? The core power source of the system. It increases the pressure of normal water to the required ultra-high working pressure (common range: 1000 - 3000 bar / 15,000 - 45,000 psi). Plunger pumps are commonly used.
Accumulator/Pulse Damper: ? Reduces pressure fluctuations from the high-pressure pump output, providing a more stable jet.
High-Pressure Piping: ? Piping that withstands ultra-high pressure (usually steel wire reinforced hoses), transporting high-pressure water from the pump to the actuator.
Actuator/Spray Gun:
Handheld Spray Gun: ? Used for small areas, complex shapes, or local repairs. Operators must wear complete protective equipment.
Rotating Nozzle: ? Installed on the spray gun or spray bar, increasing coverage area and efficiency through rotation. Commonly used for large-area planar operations.
Wall-Climbing Robot/Automated System: ? Used for large structures (such as hulls, tanks, bridges), improving safety, efficiency, and consistency. Usually integrates multiple rotating nozzles.
Nozzle: ? The core component that converts the pressure energy of high-pressure water into kinetic energy. The material is usually hard alloy (tungsten carbide) or sapphire, ruby. The nozzle aperture (usually 0.15mm - 0.8mm) and shape (fan-shaped, conical, rotating) directly affect the shape, impact force, and coverage of the jet.
Post-treatment System (Optional but Important):
Wastewater Recycling System: ? Collects wastewater generated during operation (including separated rust, old paint, etc.), performs solid-liquid separation and treatment, achieving wastewater recycling or compliant discharge. This is key to demonstrating environmental friendliness.
Vacuum Recovery System: ? Works synchronously with the spray gun, immediately removing separated waste and wastewater, keeping the work surface clean and dry (especially suitable for indoor, high-altitude, or situations requiring immediate drying).
Control System: ? Adjusts pressure, flow rate, monitors equipment operating status, and automated systems also control the robot's movement path.
III. Technological Advantages
Environmentally Friendly and Pollution-Free:
Dust-Free: ? Unlike sandblasting, which produces large amounts of harmful dust (silica dust, heavy metal dust), it avoids silicosis risk, improves the working environment, and complies with strict environmental regulations.
No Chemical Pollution: ? Pure water jetting does not use chemical solvents and does not produce toxic or harmful chemical waste or VOC emissions.
Treatable Wastewater: ? The separated waste is mainly solid rust and paint, which is easily separated and treated by physical methods such as sedimentation and filtration. The treated water can be recycled or discharged according to standards.
Zero Substrate Damage:
Pure water jetting is a "gentle" removal method, only removing loose rust and deteriorated coatings, causing almost no damage to dense, intact metal substrates (unlike sandblasting, which may cause plastic deformation of the metal surface, embedding of abrasives, and changes in stress state).
Especially suitable for processing precision parts, thin plates, substrates with hardened layers or special coatings.
Excellent Surface Treatment Quality:
It can thoroughly remove soluble salts (such as chloride ions, sulfate ions), which are difficult to completely remove by methods such as sandblasting. Salt residue is one of the main causes of early rusting (flash rust) and coating failure of new coatings. High-pressure water cleaning is an effective method for achieving high-grade cleanliness.
It can form an ideal clean, rough, and activated metal surface profile, increasing coating adhesion.
High Efficiency: ? Automated equipment (such as climbing robots) can operate continuously, with high efficiency, especially showing significant advantages in large-area planar operations. The application of rotary nozzles has also greatly improved the efficiency of manual operations.
Improved Safety:
Eliminates the risk of dust explosions (particularly important in petrochemical, shipbuilding, and other flammable and explosive environments).
Reduces the risk of operators being exposed to harmful dust and chemicals.
Automated equipment reduces risks associated with high-altitude, confined space, and other human operations.
Multi-functionality: ? By adjusting pressure, flow rate, nozzle type, and distance, it can handle various situations from light surface rust to heavy rust layers, and from ordinary paint to epoxy thick paste coatings. It can also be used for concrete roughening, paint removal, and descaling.
Cost Savings (Comprehensive Consideration):
Eliminates the expensive costs of dust collection, treatment systems, and protection.
Reduces downtime (fewer environmental restrictions, can operate in sensitive areas).
Extends coating lifespan (more thorough surface treatment).
Low waste disposal costs (mainly solid waste).
Relatively low water costs (especially treated recycled water).
V. Key Application Areas
Shipbuilding and Marine Engineering: ? Rust and paint removal from ship hulls, decks, ballast tanks, cargo oil tanks, and superstructures. High environmental requirements and strict dust control.
Storage Tanks: ? Maintenance and rust and paint removal from the inner and outer walls of crude oil tanks, chemical tanks, and LNG tanks. High safety requirements (explosion-proof).
Bridges and Large Steel Structures: ? Renovation and maintenance of steel bridges, power plant steel structures, factory steel structures, and stadiums. Reduces environmental and traffic impact.
Petrochemicals and Power: ? Rust removal and corrosion prevention on the outer surfaces of refining equipment, pipelines, reactors, heat exchangers, boilers, and desulfurization towers. Safe operation in production areas.
Manufacturing: ? Cleaning of large equipment, molds, precision parts, and pre- and post-welding parts.
Concrete Structures: ? Removal of laitance, weak layers, old coatings, and contaminants (roughening treatment) to prepare for repair or new coatings.
VI. Limitations/Challenges
High Equipment Investment: ? High initial investment cost for ultra-high-pressure pumps, pipelines, nozzles, and automated equipment.
High Operational Skill Requirements: ? Especially for handheld operations, experienced operators are needed to control distance, angle, and movement speed to achieve optimal results and avoid substrate damage (improper operation or prolonged stay under extremely high pressure may still damage the substrate).
Flash Rusting Problem: ? Clean steel surfaces treated and exposed to humid air will rust quickly (flash rust). Requires prompt drying (such as hot air drying, simultaneous vacuum recovery drying) or coating with a compatible primer (such as wet rust primer, reactive primer) within a specified time (usually a few hours).
Wastewater Treatment: ? Although environmentally friendly, it produces a large amount of wastewater containing solid waste, requiring an effective recovery and treatment system, which increases the complexity of on-site management.
Operational Environment Limitations: ? Produces a large amount of water mist and noise. Cold weather operations need to consider antifreeze. High water and electricity consumption.
Efficiency on Heavy Oxide Scales or Extremely Hard Coatings: ? For very thick and dense rolling oxide scales or some extremely hard and wear-resistant old coatings, the efficiency of pure water jetting may be lower than sandblasting, sometimes requiring higher pressure or the combination of abrasives (water jet blasting).
VII. Development Trends
Higher Pressure and Intelligence: ? Equipment is developing towards higher pressure (>3000 bar), higher flow rate, and higher reliability. Automation, robotization, and intelligence (visual recognition, automatic path planning, automatic parameter optimization) are the mainstream directions.
Green Technology: ? Continuous improvement in wastewater recycling and reuse technology, low-noise technology, and energy-saving technology.
Multi-functional Integration: ? Equipment integrating rust removal, vacuum recovery, drying, and even preliminary coating.
Expansion of Abrasive Water Jetting Applications: ? In areas where pure water jetting is limited, the application of controllable and environmentally friendly abrasive water jetting (such as using soluble and recyclable abrasives) is increasing.
Standard Improvement: ? Surface evaluation standards for high-pressure water rust removal (such as surface salt content detection and flash rust control evaluation) will be further improved.
Summary
High-pressure water rust removal (especially ultra-high-pressure pure water rust removal) is an advanced surface treatment technology that is efficient, environmentally friendly, and does not damage the substrate. Its core advantages lie in thoroughly removing contaminants (especially salts) while avoiding dust pollution and substrate damage. Although there are challenges such as high equipment costs, flash rust treatment, and wastewater management, it has become an indispensable and even preferred rust removal technology in shipbuilding, storage tanks, bridges, petrochemicals, and other fields due to increasingly stringent environmental regulations and ever-increasing demands for surface treatment quality. With the continuous advancement of equipment technology, automation levels, and post-treatment technologies, its application range will become even wider. Selecting the appropriate pressure level, equipment type, and operating process is the key to the successful application of this technology.
The 17th China International Powder Metallurgy and Hard Alloy Exhibition
The 2025 17th China International Powder Metallurgy and Hard Alloy Exhibition from March 10-12, 2025, at the Shanghai World Expo Exhibition and Convention Center, Hall H1, B425. We welcome guests to visit.
"Private custom" product design, reliable and durable finished products
"Private custom" like product design, reliable and durable finished products, professional and timely after-sales service. It is the "three basic concepts" that the company adheres to from the beginning until today ".
Experienced market research team, independent product development concept
We have experienced mature market research team, independent product research and development concept, professional design and manufacturing technology so that the company's products can be adjusted according to the specific requirements of customers timely design